This comprehensive guide examines breakthrough sustainability innovations across multiple industries, featuring expert perspectives on how these technologies are reshaping our future. From AI-powered precision agriculture to solid-state batteries and circular fashion systems, these solutions offer practical pathways to address pressing environmental challenges. Discover how these emerging technologies work together to create more sustainable systems while driving economic and social benefits.
- Next-Generation Storage Enables 24/7 Clean Power
- Advanced Thermal Management Unlocks Sustainable Technology
- Circular Fashion Systems Eliminate Textile Waste
- AI-Powered Precision Agriculture Transforms Farming Sustainability
- Direct Air Capture Turns Carbon into Resource
- Simple Solar Desalination Tackles Global Water Scarcity
- Decentralized Renewable Grids Empower Local Communities
- AI Optimizes Energy Use in Data Centers
- Low-Code Automation Cuts Energy Waste
- Large-Scale Energy Storage Makes Renewables Reliable
- Closed-Loop Recycling Transforms Medical Plastic Waste
- Solid-State Batteries Accelerate Renewable Energy Adoption
- Solutions Needed for AI’s Growing Environmental Impact
Next-Generation Storage Enables 24/7 Clean Power
As renewable energy takes center stage globally, one question continues to shape the conversation: how do we ensure reliable power when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing? The answer lies in a transformative innovation—next-generation energy storage systems.
Why Energy Storage is Critical
Solar and wind have become increasingly efficient and cost-competitive. Yet their intermittent nature has always been a barrier to full-scale adoption. Without dependable storage, homeowners, businesses, and utilities still rely on fossil fuel backups. Advanced technologies such as flow batteries and solid-state batteries are changing this. These systems make it possible to store renewable energy for extended periods—ranging from hours to days—so clean power can be delivered whenever it’s needed most.
Scalability and Flexibility
What makes next-generation storage especially powerful is its versatility. For homeowners, it enables solar energy use long after sunset, lowering utility bills and reducing reliance on the grid. For businesses, it means reliable operations, even during peak demand or outages, while advancing sustainability targets. At the utility scale, long-duration storage stabilizes entire grids, delivering resilience and security for communities across North America and beyond.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Pairing renewables with advanced storage reduces emissions and makes adoption more financially viable. With the ability to dispatch clean energy around the clock, renewable systems can compete directly with traditional power plants. This levels the playing field, accelerating the transition to a carbon-free energy landscape and supporting economic growth through new infrastructure, technology, and green jobs.
Why This Matters Globally
Next-generation energy storage addresses one of the final hurdles in renewable adoption: consistency. By making renewable energy available 24/7, we not only accelerate global sustainability goals but also build more resilient, equitable energy systems. Communities can confidently choose renewables without compromise, knowing their power supply is clean, stable, and future-ready.
At Exactus Energy, we see innovations like these as essential building blocks of tomorrow’s energy landscape. By integrating advanced storage with solar and renewable solutions, we’re paving the way for a brighter, more sustainable future—one where clean energy is no longer an alternative, but the standard.

Advanced Thermal Management Unlocks Sustainable Technology
One sustainable technology innovation with the potential for massive global impact is advanced thermal management systems for energy-intensive applications—particularly in electric vehicles, data centers, and nuclear energy.
As our world electrifies, heat has quietly become one of the most pressing barriers to sustainability. For electric vehicles, efficient battery cooling not only extends driving range and lifetime but also makes fast charging safer and more reliable. In data centers, which already consume more than 1% of global electricity, innovative solutions like liquid immersion cooling can reduce energy waste dramatically, enabling the growth of AI and cloud services without a parallel rise in emissions. In nuclear energy, compact and highly efficient microchannel heat exchangers are helping reactors operate more safely and effectively, supporting the expansion of low-carbon power.
Much of my own research focuses on serpentine geometries for cooling channels, which enhance heat transfer performance while minimizing pumping power—an approach that can be applied across EV batteries, electronics, and energy systems. This is just one example of how targeted design innovations in thermal management can multiply efficiency gains.
I see this as critically important because cooling is often the hidden enabler of sustainable progress. We can design better batteries, faster chips, or more efficient reactors, but without managing the heat they generate, their performance and lifespan remain limited. By rethinking cooling—from advanced geometries to immersion-based designs—we unlock efficiency gains across multiple sectors simultaneously.
In short, sustainable thermal management may not be as visible as solar panels or wind turbines, but it’s one of the silent technologies that will determine whether our transition to a low-carbon world is truly scalable.

Circular Fashion Systems Eliminate Textile Waste
The sustainable technology innovation I believe has the most significant global potential is a circular system within the fashion industry. This approach fundamentally transforms how products are made and what happens after consumers finish using them.
The fashion industry currently faces a sustainability crisis. According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, a truckload of textile waste is burned or buried every second. The World Economic Forum reports that fashion accounts for 10% of humanity’s carbon emissions. These numbers aren’t just statistics – they represent a real environmental emergency that requires immediate action.
A circular supply chain is a closed-loop system where products are designed from the start to be remade into new items once they’re worn out. This keeps materials in use and out of landfills.
We’ve implemented this approach through our Teemill platform, allowing brands to build e-commerce sites and sell sustainable merchandise with no stock or upfront costs. Our products are made from sustainable materials in renewable energy-powered factories, helping to cut plastic and carbon pollution. To close the loop, consumers can return their products back to us to be remade into new ones through our Remill programme. We also accept any 100% cotton clothing from any brand, in any condition (excluding denim and underwear), so we’re not only closing the loop on our own products but helping to clean up the wider fashion industry.
The key innovation is about creating an entire system that eliminates the concept of waste. What makes this technology so important is its scalability. By making this circular system available to others in the industry, we can multiply the positive impact far beyond what any single brand could achieve alone.
To truly address global environmental challenges, we need to move past the take-make-dispose model that has dominated manufacturing for too long. A circular supply chain offers us a practical, implementable path forward that can transform the fashion industry.
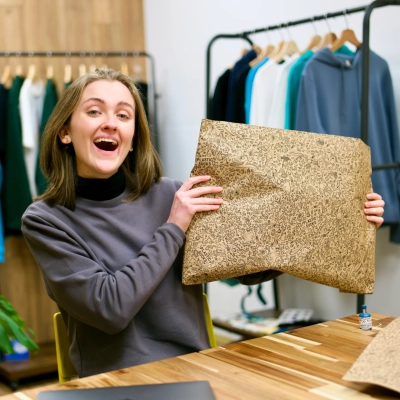

AI-Powered Precision Agriculture Transforms Farming Sustainability
One sustainable technology innovation I believe could have a significant global impact is precision agriculture powered by AI and IoT. I saw this closely while working with a startup focused on agri-tech, and it completely shifted how I think about sustainability in farming. Farmers often rely on traditional practices that use large amounts of water, fertilizer, and pesticides without knowing exactly how much is needed. This not only raises costs but also harms the soil and environment over time.
The startup introduced a system where sensors were placed in the fields to measure soil moisture, nutrient levels, and crop health in real time. AI models then analyzed the data and recommended exactly how much water or fertilizer was required, down to specific parts of the field. The result was remarkable. Water usage dropped by almost half, crop yields improved, and the farmers spent less on resources. It was a win on every side, both economically and environmentally.
What struck me most was how quickly farmers embraced the change once they saw the benefits. Technology that seemed intimidating at first became a trusted partner in their daily work. Beyond one farm or region, the global impact of adopting precision agriculture at scale could be enormous. It addresses food security, conserves natural resources, and reduces the environmental footprint of farming.
As managing consultant and founder of SpectUp, having worked with multiple startups in sustainability and technology, I would suggest that innovations like this show us the path forward. When technology solves a real problem and delivers immediate value, adoption follows naturally and the world moves a step closer to sustainable growth.

Direct Air Capture Turns Carbon into Resource
Direct Air Capture (DAC) feels like a real turning point in the climate conversation. For years, I heard the same focus repeated over and over: reduce emissions, cut back, and stop carbon from entering the air. That’s obviously important, but I kept wondering: what about the carbon that’s already there? DAC finally answers that question. It gives us a way not just to slow the problem, but actually start reversing it.
What really excites me is that DAC isn’t just an environmental solution; it also has an economic upside. The first time I learned that captured CO2 could be used to make things like sustainable jet fuel, building materials, and even plastics, it completely changed my perspective on carbon. It’s no longer just a harmful byproduct we need to bury underground; it can actually become a resource. That shift creates a powerful incentive for businesses to invest, because they’re not just spending money to reduce harm—they’re creating value.
To me, that’s what makes DAC so important. It’s not just another climate technology; it’s the beginning of a new industry. One that takes an old problem and transforms it into new opportunities, aligning what’s good for the planet with what’s good for the economy. That’s the kind of big-picture thinking we need if we’re serious about tackling climate change at scale.

Simple Solar Desalination Tackles Global Water Scarcity
A sustainable innovation I think doesn’t get nearly enough attention is low-tech solar desalination. Most people picture massive, industrial desalination plants—expensive, energy-hungry, and limited to wealthy regions. But there’s a quieter wave of innovation happening with small-scale, solar-powered systems that can turn brackish or seawater into drinkable water at a household or village level.
Why do I think it’s huge? Because water scarcity isn’t just an environmental issue—it’s a trigger for conflict, migration, and health crises. If you can decentralize water production and make it as simple as setting up a solar still in a rural community, you remove one of the most destabilizing forces in the 21st century. It’s not just about hydration; it’s about giving people the stability to farm, stay in place, and build local economies instead of being forced to uproot.
What makes this exciting is the elegance of it: no giant infrastructure, no complex upkeep, just sunlight and smart design. It’s sustainability at its most practical—quietly life-changing in regions where centralized grids and billion-dollar projects will never reach.
To me, that’s the kind of innovation with global impact: not the flashiest, but the one that makes the basics—clean water, stability—accessible to the billions who need it most.

Decentralized Renewable Grids Empower Local Communities
We believe that decentralized renewable grids can significantly impact the world. Our team is inspired by innovations that allow others to generate and manage their own clean energy locally. This approach reduces energy loss during transmission, strengthens resilience, and gives people more control over their resources. By producing power where it is needed, communities can rely less on centralized systems and respond faster to local demands.
Access to reliable electricity is still limited in many parts of the world. Decentralized renewable systems not only reduce dependence on fossil fuels but also promote energy fairness. When communities have direct access to clean power, they can improve education, grow local businesses, and enhance healthcare services. This approach supports sustainability while empowering people to shape their own future through energy independence and local solutions.

AI Optimizes Energy Use in Data Centers
One sustainable technology that, in my opinion, has the potential to completely transform the global economy is AI-driven energy optimization in data centers and heavy industry. Data centers currently consume almost 2% of the world’s electricity, and this percentage is steadily increasing. By using machine learning to balance workloads, optimize cooling, and cut down on wasted power, we have already witnessed cases where energy use drops by double digits without the need to build a single new plant.
Given that digital infrastructure is growing far faster than renewable energy, I believe it is essential. Efficiency is the “hidden fuel” that buys us time to increase the use of renewable energy.

Low-Code Automation Cuts Energy Waste
One sustainable tech innovation with massive global impact potential is low-code automation for energy efficiency. Most companies are still wasting huge amounts of energy through duplicate systems, manual approvals, and servers running around the clock for no reason. Every one of those inefficiencies burns carbon as well as cash.
I believe it’s crucial because operational waste is a significant sustainability issue. Automation can shut down idle resources, push customers to lower-energy channels like chatbots, or digitize paper-heavy approvals. In fact, the IDC projects that by 2026, digital transformation will lower global CO2 emissions by 20%.
We see our role as helping companies eliminate that waste at scale. By building leaner processes, automating routine tasks, and reducing unnecessary infrastructure, we help clients shrink their footprint while helping them hit their targets.

Large-Scale Energy Storage Makes Renewables Reliable
One sustainable innovation with the potential for enormous global impact is large-scale energy storage. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are abundant, but their intermittent nature limits reliability. Affordable, long-duration storage technologies—such as advanced batteries and green hydrogen—can bridge this gap by making clean energy consistently available.
This is critical because stable access to renewable power directly reduces dependence on fossil fuels, lowers emissions, and creates the foundation for sustainable growth in both developed and emerging economies. The ability to store energy at scale transforms clean power from an alternative option into a dependable global standard.

Closed-Loop Recycling Transforms Medical Plastic Waste
One sustainable innovation with real global impact is the development of closed-loop recycling for medical and industrial plastics. Each year, enormous amounts of plastic waste are incinerated or sent to landfills. Perfecting recycling systems that return these materials to safe and usable products can transform many industries. This approach reduces the pressure on natural resources and helps address the growing environmental problems caused by single-use items. By rethinking the life cycle of materials, we can create practical and responsible solutions.
Healthcare alone contributes significantly to plastic consumption. A system that turns waste into raw material manages costs and strengthens supply chains. It also ensures that critical operations can continue without compromising environmental responsibility. To me, this is more than a technological improvement. It represents a shift toward circular thinking that protects the planet while reliably and efficiently meeting urgent human needs.

Solid-State Batteries Accelerate Renewable Energy Adoption
One sustainable technology innovation that could have a major global impact is next-generation energy storage, such as solid-state batteries. These allow renewable energy from solar and wind to be stored more efficiently and used when demand is high, solving one of the biggest limitations of clean energy.
It’s important because reliable storage can accelerate the global shift away from fossil fuels, reduce grid instability, and make renewable power accessible at scale. This single advancement can support cleaner transportation, smarter cities, and more resilient energy systems worldwide.

Solutions Needed for AI’s Growing Environmental Impact
One sustainable technology innovation that we need, but don’t exactly have yet, is a way to minimize AI’s environmental usage. AI has only become used in this widespread manner in the past few years, but the environmental impact it’s had has already been significant. And it’s projected to only get more and more severe as AI usage continues to grow. It requires a ton of water, uses massive amounts of energy, and AI data centers can have big effects on their local areas. This is a problem that needs a solution soon.